Step-by-Step guide for patient. Millions of people in the world use insulin injections. Insulin drugs are designed to manage blood glucose rates in male & female persons with type I diabetes (an ailment when the body doesn’t synthesize insulin, those who suffer from type II diabetes (an ailment characterized by impaired insulin production), and females with gestational diabetes when these diseases cannot be treated only by oral medications.
In this article, we will tell you why might you need to make insulin injections and how to make them properly in order to avoid possible complications and provide the maximum therapeutic effect.
Why Might You Need to Use Insulin Injections?
Over time, persons with diabetes may develop complications associated with a persistent high level of glucose in the blood. They include nerve damaging (which can lead in particular to impairment of sexual function), eye ailments (diabetic retinopathy), heart diseases, stroke, etc. Insulin injections replenish the missing amount of natural insulin in the body. This helps the body use glucose and lower blood sugar rates. The use of injectable insulin (and possibly other drugs) in combination with proper nutrition, lifestyle correction, and periodic blood glucose checking helps patients improve their health, feel good, and prevent the development of dangerous complications.
Forms of Insulin & Insulin Injections
Generally speaking, insulin can be long-term, short-term, and mixed (include short-acting & long-acting meds). Short-term form quickly releases from fat tissue providing a rapid effect. It is designed for covering the blood sugar elevation from eating. Short-term insulin is represented by Humalog, Nobolog, and Apidrameds. Long-term type of the drug is released over a long period of time.
For instance, Insulin Glargine(Lantus) is a long-acting drug. It provides a slow and stable effect (18 to 26 hours) without sharp fluctuations in insulin levels in the blood. Lantus insulin starts to act several hours after making injections. It is administered once a day, preferably at approximately the same time.
The form of the medicament should be chosen by a healthcare professional and patient jointly, depending on different factors, such as lifestyle choices, body’s response to insulin, age, individual preferences, etc. Choose your diabetes medication online by link: iacopharmacy.com/canadianpharmacy/canadianinsulin-com.html
Insulin is produced in different forms: vials, prefilled dosing devices (pens), and cartridges, which should be placed in pens. If the drugs come in vials, patients should use syringes in order to make injections. Insulin types (U-100 and U-500) should match with markings on the syringe. It is necessary to use needles & syringes of the same brands and models.
It should be noted that the length of traditional needles for insulin shots is almost 13 mm. According to recent research, shorter needles (4-8 mm) have the same effectiveness. It means that now insulin injections become less painful than previously.
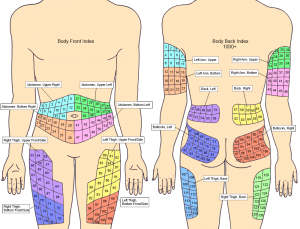
Sites for Insulin Injections
Injections with the drug should be done into the fatty (adipose) tissue under the skin (the so-called subcutaneous injections). It means that a short needle is inserted into the layer between the skin & muscles. Make sure the needle is injected at a small depth, right under the skin. If you enter it deeply, you will reach the muscle. This can cause pain and lead to an acceleration of insulin absorption in the body. As a result, you may suffer from hypoglycemia.
Persons who use the medicament on an everyday basis should alternate injection sites. Permanent damage of the same place can lead to lipodystrophy (lack of fat in a certain place or vice versa, the expansion of adipose tissue). These changes can interfere with the absorption of insulin.
Places for injection can be selected on the belly, also you can make shots into buttocks, hips and triceps area.
- Abdomen. The most recommended place for injecting the medication is the abdominal area (excluding a 2-inch radius near the navel). First, the active agent is absorbed quickly from this place. Secondly, it is easier to inject into the abdomen than into other places (this is the most accessible area).
- Thighs. Injections of the drug can be made to the inner or outer thighs, at points located about 10 centimeters from the top of the leg and 10 centimeters above the knee.
- Triceps area. Injections can be done in the fatty area on the back of the hand between the elbow and shoulder. However, you are not recommended to do it by yourself, ask someone to help you.
Modern mobile applications, such as ShotPut, can significantly help patients with injection places rotation. They help patients keep track of the sites & rotate them. The apps also inform patients about the last injection site and where to make an injection next time. A person can program his/her shot schedule and an app will tell his/her when it is time to inject.
Using prefilled pens may be more convenient for you.
For instance, Lantus Insulin comes in 2 forms: as a vial & syringe and as prefilled SoloSTAR? pen. The pen has a special dosage selector, which facilitates dose selection.
How to Make the Injection ? Step-by-Step Instruction
 First check the condition and quality of the drug. If you store it in the refrigerator, remove it beforehand so it warms up to room temperature. If the medication is slightly unclear, roll it between the hands, but do not shake to avoid bubbles’ formation. Do not use thickened or cloudy preparation.
First check the condition and quality of the drug. If you store it in the refrigerator, remove it beforehand so it warms up to room temperature. If the medication is slightly unclear, roll it between the hands, but do not shake to avoid bubbles’ formation. Do not use thickened or cloudy preparation.
Follow the steps below:
- Gather all the items necessary for injection. These include an ampoule with insulin, alcohol swabs, needles & syringe, gauze & bandage (just in case). Wash hands with soap & warm water. Remove caps from the bottle with the drug and from the needle.
- Draw in the syringe as much air as insulin units will be needed to be injected in later. Let the air go into the ampoule. The air replaces the quantity of the fluid you’ll withdraw.
- First, draw a little more insulin into the syringe than necessary. This is done to make it easier to remove air bubbles trapped in the syringe. To do this, tap on the syringe body slightly and release the excess amount of the drug together with air back into the vial.
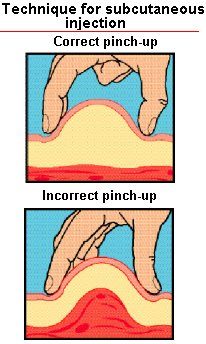
- Wipe the zone of the skin, where you will give a shot, with alcohol, wait until it dries. With your thumb and forefinger, hold the skin into the fold (by using a pinch-up technique) as shown in the picture below. This is also done to reduce the likelihood of making the shot into the muscle. When you use the shortest needles, this is not necessary (especially if you’re injecting the drug into the belly).
- Insert the needle into the skin fold perpendicularly to the surface or at an angle of 45? (depending on the adipose tissue amount under your skin; if you you’re skinny, it is better to make a shot at a 45? angle).
- Holding the fold, press the syringe plunger to the extreme position.
- Wait for a while after injecting insulin, then remove the needle.
- Do not rub the site of the shot. Bleeding from the injured site may be observed. To stop it, you may use a gauze and bandage.
Insulin Injection During Pregnancy
Insulin shots in pregnant females are commonly made into the back of the arm or into thighs, not in the abdominal area (for obvious reasons ? because future moms are afraid they can hurt the baby). However, it’s unlikely that an insulin needle cause problems by hitting the baby. In early stages of pregnancy, women can make shots as they usually do. But in late stages, an injection procedure may be difficult due to stretched skin. In such cases, females should choose areas at the belly side or at other places on the body.
Giving Injections to Children
The procedure of giving insulin shots to children is usually the same as that to adults. However, some children may not want to feel the needle. In such cases, you may use an indwelling subcutaneous catheter, which is a soft tube inserted into the skin site where injections will be given. When the time of injection comes, you will insert the needle into the catheter, not into the skin. The subcutaneous catheter is used minimum for three days before inserting the new one.